In this article, we will discuss various OSPF Packet types or Message types that are used by the OSPF Routing Protocol. There are several messages which are used in OSPF in order to share data bits from one router to another router.
Quick Overview to OSPF Packet
Before we move to the detailed discussion, let’s take a look at various Messages used in the OSPF protocol. There are 5 different messages which are used in the OSPF process. They are:
- Hello
- DBD (Database Description)
- LSR (Link State Request)
- LSU (Link State Update)
- LS-Ack (Link State Acknowledgement)
Now, we will discuss these messages one by one.
Hello
Hello, the message is also known as the Type-1 packet. In OSPF, Hello Message is used for:
- Neighbor Discovery
- Keep Alive (by default timer is 10 seconds)
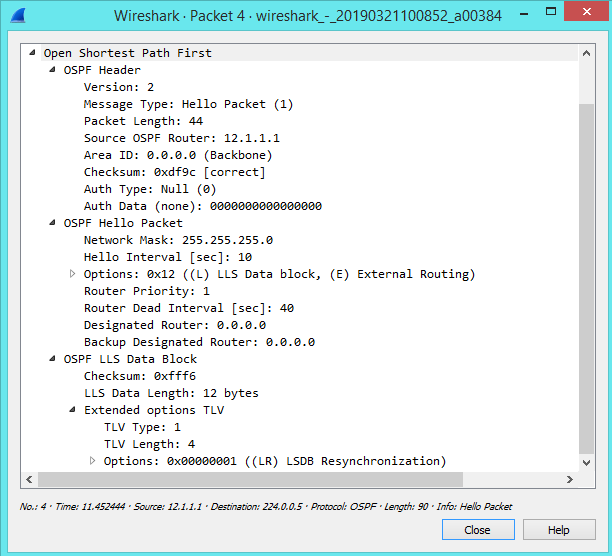
However, there are various contents that are sent from one router to another router. You can also see all these contents with the help of Wireshark. The contents of Hello Messages are::
- OSPF Version (v2 by default in IOS v12 and v15)
- Type 1 (indicate a Hello message)
- Packet Length
- Router-ID
- Area-ID
- Checksum
- Authentication Type
- Authentication Data
- Network Mask
- Hello Interval
- Dead Interval
- Priority
- Neighbor Router-ID
- DR & BDR Router-ID
- Stub-Flag
- Neighbor Router Priority
As shown in Wireshark Image, the Hello message of the OSPF protocol is multicast on 224.0.0.5.
You can also read: EIGRP Packet Types
DBD (Database Description)
DBD stands for Database Description. This message is used to synchronize LSDB (Link State Database) between two Routers. Along with this, this message helps in neighbor formation and MTU size negotiation. This message usually used in the Ex-Start state.
LSR (Link State Request)
LSR stands for Link State Request. It is used to request specific link-state records from an OSPF neighbor router. However, this is initiated by the OSPF Master which is chosen in Ex-Start state.
LSU (Link State Update)
LSU (Link State Update), is a reply to LSR (Link State Request). When the OPSF Master router, sends LSR to slave router, then Slave Router provides Link State Records to Master Router using LSU (Link State Update) message.
LS-Ack (Link State Acknowledgement)
As the name suggests, the LS-Ack message is used for acknowledgment purposes. This acknowledgment is for LSU message. With the help of this message, we can examine that the receiver end OSPF router successfully receives LSU (Link State Update).
OSPF Neighborship Requirements
There are several conditions or requirements which should be met in order to become OSPF neighbors. Basically requirements are:
- Router-ID Must not match
- Area-ID must match
- Authentication Types must match
- Authentication Data must match
- Subnet Mask must match
- Hello and Dead Interval must match
- The stub – flag must match
- MTU size must match
Summary
In this article, we discussed OSPF Messages which are used by the OSPF protocol in order to send and receive data streams from neighbor routers. We also discussed some conditions which must be compiled in order to become neighbors of each other.
Did you find this article helpful? Please leave a comment in the comment box!
Nice and very helpful artical is this.
Hi Nitin,
It’s really great to hear this!
Good Article. No fluff. To the point. Clear information.