DORA is a process used by DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). DHCP provides an automatic IP address to Hosts that want to connect to a network. In this article, we will discuss the DORA process in detail.

What is the DORA Process in DHCP?
DORA is a process that DHCP uses to provide an IP address to hosts or client machines. The DORA process has four messages.
- Discover
- Offer
- Request
- Acknowledgment
Now, take a look at the below diagram. This diagram will show you how the client and server exchange these messages.
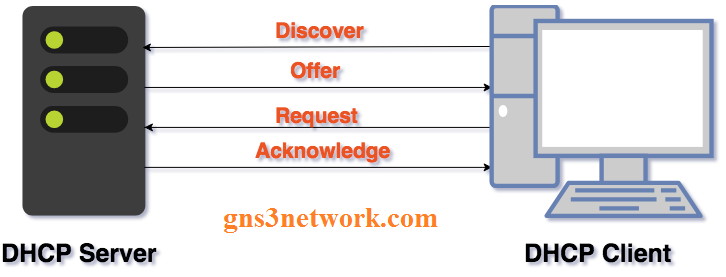
Now, we will look at exactly what happens when a DHCP client requests an IP address from DHCP Server. Some messages are exchanged between the DHCP Server and Client. These messages are explained below.
Keypoint: All DHCP Messages are broadcast at Network Layer (i.e Layer 3).
DHCP Discover Message – The Dora First Message
Discover Message is the first message of the DORA process. In this message, the DHCP client wants to discover a DHCP Server and sends a DHCP Discover message. Different fields of Discover message are :
Source IP: 0.0.0.0
Destination IP: 255.255.255.255
Source MAC: DHCP Client Machine MAC Address
Destination MAC: FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF
So, we can say that the DHCP Discover message is always broadcast at the network and data link layer.
DHCP Offer Message – The Dora Second Message
As soon as the DHCP Server receives the Client Discover message, the DHCP server replies to the DHCP client as an offer message.
Source IP: DHCP Server IP Address
Destination IP: 255.255.255.255
Source MAC: DHCP Server Machine MAC Address
Destination MAC: DHCP client MAC Address
Now, as you can see, still the Destination IP address in the DHCP Offer Message header has a broadcast IP address. This is because the client didn’t get an IP address from DHCP Server. But, this time, this message is broadcast on Network Layer only.
DHCP Request Message – The Dora Third Message
The DHCP client machine receives the DHCP Offer message and replies with a DHCP request message. This message tells the DHCP server that I’m fine with this IP address. Please allocate this IP address to me. The DHCP Request Message header has the following main fields:
Source IP: 0.0.0.0
Destination IP: 255.255.255.255
Source MAC: DHCP Client Machine MAC Address
Destination MAC: DHCP Server MAC Address
Now, as you can see, still Client Source IP address is 0.0.0.0. This is because the client still didn’t get an IP address from DHCP Server. Also, this message is broadcast only at the network layer of the OSI Model.
DHCP Acknowledge Message – The Dora Fourth Message
DHCP acknowledge message is the last message of the DORA process. It is sent by the DHCP Server to the DHCP Client. This message is a reply to the DHCP Request message. This message header has the following main fields:
Source IP: DHCP Server IP Address
Destination IP: 255.255.255.255
Source MAC: DHCP Server Machine MAC Address
Destination MAC: DHCP client MAC Address
After this message, the DHCP client will get an IP address. This message has broadcast at the network layer but unicast on the Data Link layer.
Understanding DORA Using Video Demonstration
Continue Reading
- How to configure Palo Alto Networks Firewall as a DHCP Server
- What is the difference between TCP/IP and the OSI Model
- OSI Model – 7 Layers Explained in detail
- TCP | Transmission Control Protocol | Explained in detail – 2024
- UDP | User Datagram protocol – Explained in detail – 2024
- Cisco line vty 0 – 4 Explanation and Configuration | VTY | Virtual Teletype
References
Summary
DORA is a sequence of messages of the DHCP process. The DHCP Server and DHCP Client exchange some messages and after that, DHCP provides an IP address to the DHCP client.
Did you find this article helpfu? Please share this article on social platforms like facebook and shows us some love 🙂
Can you please share wireshark packet capture.
I see 3 @ https://wiki.wireshark.org/SampleCaptures
Beneficial